In pursuing energy efficiency and environmental sustainability, an often overlooked ally emerges—reflective insulation. In this comprehensive guide, we aim to be your definitive resource on this insulation technology, which has been revolutionizing thermal insulation techniques for decades.
We’ll cover every aspect of this innovative material, from its scientific principles and types to real-world applications and best practices.
Whether you’re an industry expert, an architect or a contractor looking to make an informed decision, reflective insulation can be a game-changer in your energy-saving efforts.
What is Reflective Insulation?
In the competitive market for insulation materials, reflective insulation rolls stand out as a high-performing, cost-effective and versatile option that addresses a specific yet crucial aspect of thermal management—radiant heat transfer.
Originating in the mid-20th century, this technology utilizes advanced materials like aluminum foils, polyethylene bubbles, plastic and reflective films. But what sets it apart is that, unlike traditional insulation materials focusing solely on conductive and convective heat flow, reflective insulation is also engineered to target radiant heat—a form of energy that travels through the air from heat sources.
From a product standpoint, this unique focus on all three modes of heat transfer makes reflective insulation an ideal choice for a wide range of applications—from commercial buildings and residential homes to specialized industries like aerospace. Its ability to reflect up to 94-97% of radiant heat ensures optimal thermal performance and greater comfort in areas across the envelope. It offers significant energy savings and is a key selling point for any stakeholder in the construction or renovation process.
Composition and Different Types of Reflective Insulation
One size does not fit all when it comes to thermal insulation. Reflective insulation is no exception, offering a range of compositions and types to meet varying needs and applications. The core materials and construction methods are meticulously designed to optimize performance, durability, and ease of installation. Let’s break down the primary types:
Single Bubble
The Single Bubble is the most basic yet effective form of reflective insulation. It consists of a single layer of air bubbles sandwiched between two highly reflective metalized film surfaces.
A version with one side consisting of a premium white polymer film offers an insulation solution that also doubles as an attractive ceiling for metal structures or post-frame buildings. Its lightweight nature makes it easy to handle and install, while its reflective surfaces offer up to 94% radiant heat reflection.
Double Bubble
The Double Bubble option is the go-to for those seeking enhanced thermal performance. It features two layers of air bubbles between the reflective surfaces, providing additional strength and insulation value.
This type is particularly well-suited for commercial and industrial applications where higher R-values are required. The added layer also provides increased durability, making it a long-lasting solution for demanding environments.
Both types of reflective bubble insulation offer a vapor retarder solution for those seeking to reduce condensation in their buildings.

Reflective Foam
This type of reflective insulation is a composition that incorporates a layer of foam between reflective surfaces to add insulation value. It is designed to offer the benefits of both traditional foam insulation and the reflective properties of materials like aluminum foil and reflective films.
It’s typically used in scenarios where both insulation against temperature extremes and the reflection of radiant heat are desired to keep it from escaping buildings in the winter and minimize solar heat gain in the summer.

Reflective Single and Multi-Layer Foil Insulation
Single- and multi-layer options minimize heat transfer in masonry and other commercial building applications. They operate by reflecting radiant heat, the primary mechanism of heat movement within reflective air spaces.
Single-layer Design: This option is constructed from a single layer of reflective material, typically aluminum foil. It offers effective performance but may provide less insulation than the multi-layer options. Consider this option for its straightforward functionality.
Multi-layer Design: This system comprises multiple layers of reflective material interspersed with insulating layers. This configuration delivers exceptional insulation performance, making this insulation choice an approach that positions your building for maximum energy efficiency and comfort.

Understanding the different compositions and types is crucial for recommending the most effective insulation solution for specific projects. Each reflective insulation type has its unique advantages and limitations, and the choice often depends on factors like the intended application, required thermal performance, and budget constraints.
How Reflective Insulation Works
Understanding the how of reflective insulation is essential for both industry professionals and end-users. Let’s take a look at the breakdown of the scientific principles that drive reflective insulation’s exceptional thermal performance.
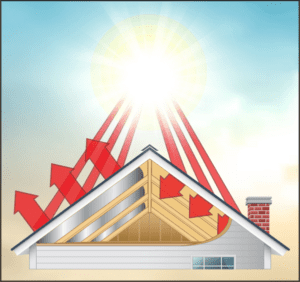
Radiant Heat Reflection
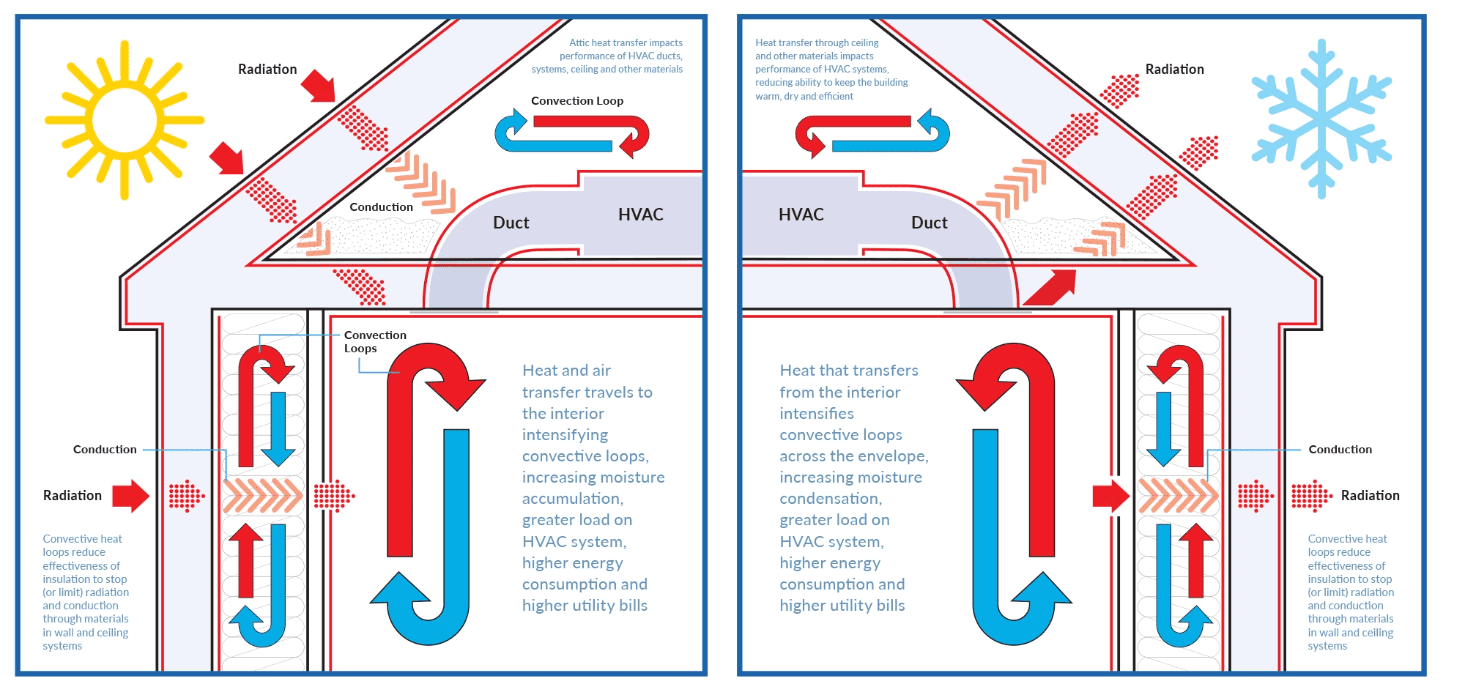
Radiant heat reflection is the cornerstone of reflective insulation technology. Unlike traditional insulation materials that primarily focus on slowing down conductive and convective heat transfer, reflective insulation also addresses radiant heat. It does so by reflecting a significant portion of radiant heat—up to 94%-97%, depending on the material and design—back to its source, thereby minimizing heat gain or loss.
Thermal Performance
The thermal performance of reflective insulation is quantified by two key correlating metrics: emissivity and reflectivity. Emissivity measures how efficiently a material emits heat, while reflectivity gauges its ability to throw back heat rather than absorb it. Foil and reflective films have a low emittance (low-e) (typically 0.03-0.06) meaning very little radiation passes through the surface material. The lower the emissivity value of a reflective surface, the higher its reflectivity (typically 0.94-0.97) which translates to blocking 94%-97% of heat transfer to keep buildings cooler in the summer and warmer in the winter. The low-e surfaces of reflective insulations and barriers indicate superior thermal performance.
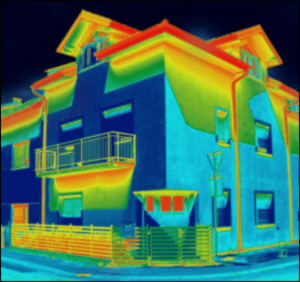
Layers and Composition
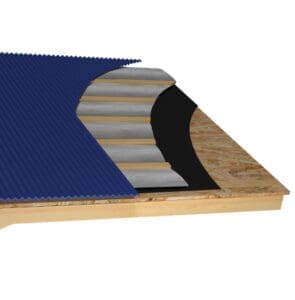
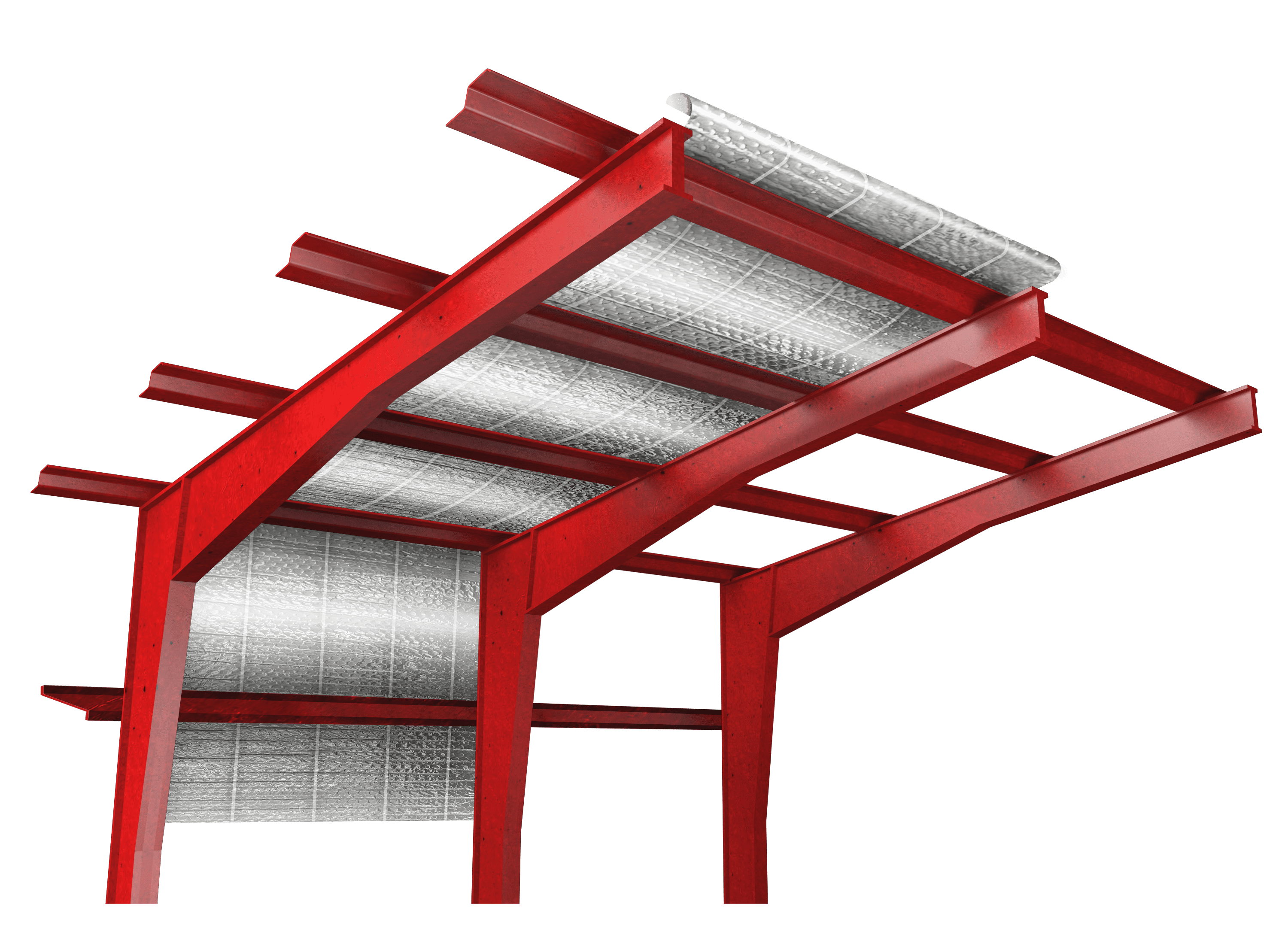
Modern reflective insulations are often multi-layered to enhance both durability and performance. The surface(s) or one or more inner layers consist of a reflective material, usually aluminum foil or metalized film, designed with other layers such as polyethylene bubbles, foam, skrim, or other insulating materials.
This multi-layered composition improves thermal performance and adds structural integrity to the product, making it more resilient to wear and tear.
The interplay between these factors—radiant heat reflection properties, thermal performance metrics, and multi-layered composition—determines the efficacy of reflective insulation in various applications. Understanding these nuances is crucial for making informed decisions, whether you’re specifying materials for a large commercial project or seeking to improve the energy efficiency of a residential property.
Where to Use Reflective Insulation
Reflective insulation’s adaptability makes it a versatile choice for a wide range of applications, each presenting its own set of thermal challenges and requirements. Understanding the primary areas where this innovative material can be most effectively deployed is crucial.
Where to install reflective insulation often depends on various factors, including thermal requirements, space constraints, and budget considerations. Being well-versed in these applications allows for more informed decision-making, whether you’re an architect, a contractor, or a product manager overseeing insulation solutions.

Commercial Applications
In the commercial sector, reflective insulation is increasingly becoming a go-to solution for thermal management. Its superior radiant heat reflection capabilities and cost savings make it ideal for large-scale applications like warehouses, manufacturing facilities, and office buildings.
Here, the focus is not just on thermal performance but also on long-term durability and ease of maintenance.
Specialized Uses
Beyond traditional commercial and residential applications, reflective insulation is used in specialized industries such as aerospace and automotive. The material’s lightweight nature and high thermal efficiency are invaluable in these sectors.
For instance, it’s commonly used in spacecraft for its ability to handle extreme temperature variations.

Residential Applications
When it comes to residential applications, reflective insulation offers a multitude of benefits. It’s commonly used in attics, basements, and crawl spaces, but its versatility doesn’t stop there.
With an increasing focus on green building practices, reflective insulation is also being used in walls and under floors to maximize energy efficiency and contribute to a home’s overall thermal envelope.
Installation Techniques and Best Practices
Like all insulations, proper installation is as critical as the material itself when it comes to maximizing the effectiveness of reflective insulation. Understanding the best practices for installing reflective insulation will ensure optimal performance and building resilience.
Orientation
The orientation of the reflective surface plays a pivotal role in the insulation’s effectiveness. With its low emissivity, the shiny side should face an enclosed air cavity or an adjacent air film to reflect radiant heat effectively. Incorrect orientation can significantly compromise the material’s thermal performance.

Seams and Overlaps
Ensuring overlaps and airtight seals is crucial for both moisture control and maintaining a continuous reflective surface. Specialized tapes or sealants are often used to secure seams, and it’s advisable to overlap seams by at least 2 inches for best results. Attention to detail here can make or break the insulation’s long-term effectiveness.

Ideal Reflective Air Space
A minimum air space of 3/4″ adjacent to the reflective surface is recommended for optimal performance. The direction of heat flow, orientation of installation, and types of insulations used in combination should be considered to meet performance and compliance in each climate zone and municipality. When used facing enclosed air cavities with 3/4″ to 6″ or more of an air gap, the reflective material enhances the air space to provide R-value and insulating benefits beyond simply a radiant barrier. In confined spaces, it’s crucial to maintain this minimum air gap to ensure the reflective insulation performs as intended.
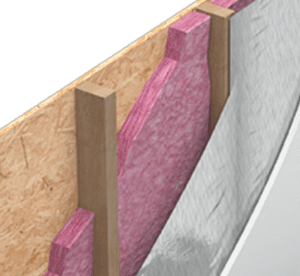
Reflective Insulation vs. Radiant Barriers
In thermal management, both reflective insulation and radiant barriers are viable options. While often perceived to be used interchangeably, they serve different purposes and are suited for different applications. Understanding the distinctions between these two materials is crucial for making informed decisions.
Material Thickness
Reflective insulation has varying degrees of thicker composition due to its multi-layered structure. This often includes one or two layers of foil that expand inside the cavity, interior layers of single or double polyethylene bubbles, or polyethylene foam core. On the other hand, radiant barriers are generally thinner and consist mainly of flexible sheet reflective aluminum foil or films. Both types are designed to significantly reduce heat transfer.

Primary Function
The primary function of radiant barriers is to reflect radiant heat, thereby reducing heat gain in the summer and heat loss in the winter. Reflective insulation, however, serves a dual purpose: it reflects radiant heat and reduces convective and conductive heat transfer. This makes reflective insulation a more versatile option for a broader range of applications.
Installation
Radiant barriers are often installed in attics, stapled to rafters, or laid with furring under metal roofs. They are generally easier and quicker to install but are limited in their range of applications.
Reflective insulation requires more careful installation, including considerations for orientation, air gaps, and amount of enclosed air space. Its versatility allows for use in many areas across the building envelope, including walls, HVAC ducts, ceilings, and floors—commonly used across all markets in residential, commercial, industrial, and institutional buildings.
Benefits and Real-World Applications
Reflective insulation offers more than just thermal management; it brings a host of benefits that have real-world implications for both the environment and your bottom line. As field experts, we understand this innovative material’s multifaceted advantages.

Energy Efficiency
One of the most compelling benefits of reflective insulation is its contribution to energy efficiency. By stopping an average 94-97% of radiant heat transfer, it significantly reduces the load on HVAC systems, and may prolong the life of HVAC systems. Less load leads to lower energy consumption and, consequently, reduced energy bills, which can translate to thousands of dollars in annual savings for commercial building owners or tenents.

Environmental Stewardship
Reflective insulation is not just good for your wallet; it’s good for the planet. Reducing energy consumption directly contributes to lowering carbon emissions, making it an eco-friendly choice for those looking to build or renovate sustainably. Many reflective insulation products are also made from recycled materials, adding another layer to the environmental benefits.

Cost Savings
While the initial investment in quality reflective insulation may be higher than other traditional insulation materials, the long-term benefits are substantial. Reduced energy bills and lower HVAC maintenance costs mean that the material often pays for itself within a few years. Additionally, the durability ensures that replacement costs are minimal, making it a financially sound choice for long-term projects.
The benefits of reflective insulation extend far beyond your building’s thermal performance and comfort. Understanding these benefits is crucial for architects and builders concerned with the materials and assemblies that support more sustainable, resilient buildings.
The FI-FOIL® Reflective Insulation Advantage
When it comes to reflective insulation, FI-FOIL® stands behind our quality, integrity, and innovation. But what truly sets us apart are the unique offerings that provide immediate and long-term value. If you’re an architect, builder, contractor, or distributor, FI-FOIL® reflective insulations and barriers offer a comprehensive solution that addresses your immediate needs—as well as—long-term goals.